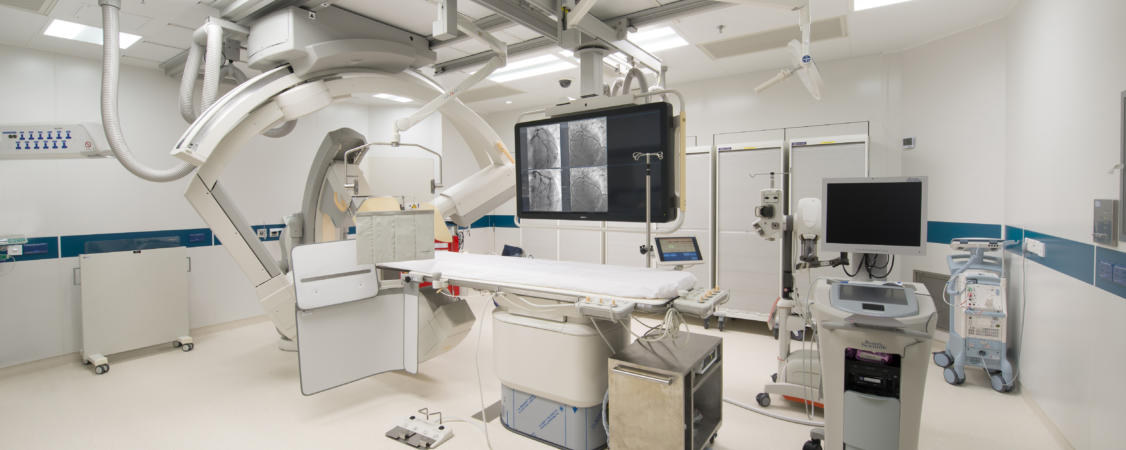
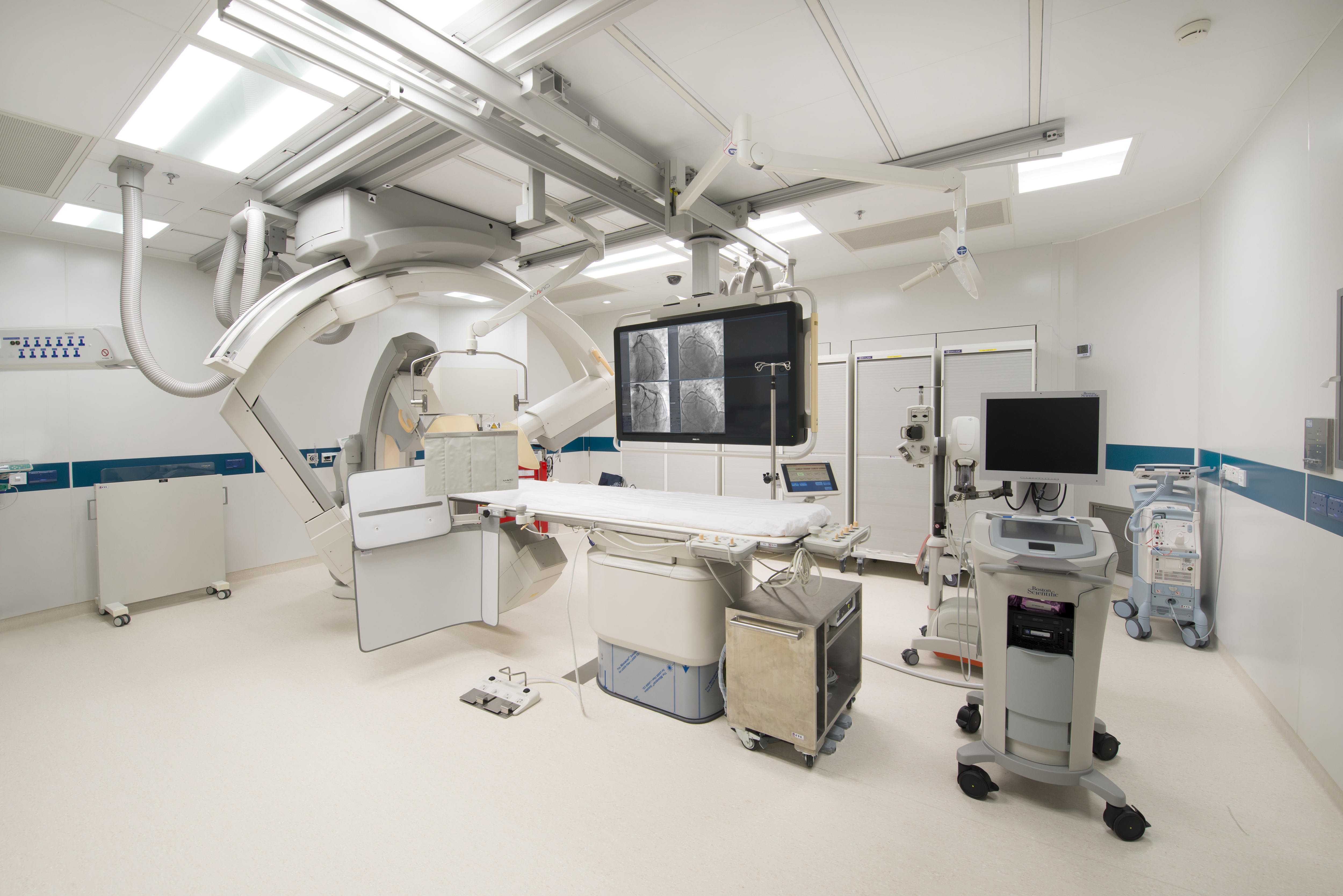
Cardiac Catheterization & Intervention Centre
With operating theatre standard, our Cardiac Catheterization & Intervention Centre is equipped with advanced integrated X-ray and coronary artery intravascular imaging modalities, i.e., intravascular ultrasoun (IVUS) and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), invasive functional assessment with coronary fractional flow reserve, providing patients with invasive procedures, such as percutaneous transluminal coronaryangioplasty and stenting, electrophysiological study, radiofreqency ablation, pacemaker implantation etc. In addition, our Cardiac Catheterization & Intervention Centre provides “24-hour emergency operation service” to cater to patients’ emergency needs.
Treatments We Offer
What is Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA)?
Pulsed Field Ablation is the latest technology used to treat paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (arrhythmia / irregular heartbeat). The Centre is equipped with the only commercially available PFA system approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Research indicates that approximately 70% of atrial fibrillation originates from abnormal electrical activities caused by active cells in the area of the pulmonary veins-left atrial junction. By ablating the tissue surrounding the pulmonary veins, these abnormalities can be blocked from entering the left atrium. However, traditional ablation methods, such as radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation, may indiscriminately destroy tissues near myocardium including the oesophagus and nerves. Complications such as oesophageal perforation can even lead to immediate death.
The recently-introduced PFA marks a breakthrough in atrial fibrillation treatment. It utilises short bursts of high-frequency, high-voltage electrical pulses to create small pores in the surface of atrial cells, leading to the death of the abnormally active cells. Compared to traditional ablation techniques, PFA minimises the indiscriminate risk of collateral damage, and hence reduces the risk of complications. Data show that 80% of patients do not experience a recurrence within a year, providing a more convenient, faster and safer ablation option.
Why PFA may be performed?
Studies have found that atrial fibrillation patients who can restore normal heart rhythm within the first year after onset are at a lower risk of stroke, heart attack, heart failure and cardiac death, compared to those who only have their heart rate controlled. For patients with a history of heart failure, even if the atrial fibrillation lasts for a short period of time, it is crucial to maintain a normal heartbeat through procedures such as PFA to reduce mortality risk.
PFA can also be performed with three-dimensional imaging to eliminate abnormal atrial tissues in the pulmonary veins area and beyond, catering to the needs of different patients.
Echocardiography is a technique that visualises the heart using ultrasound waves. A transesophageal echocardiogram(TEE) is a procedure that consists of insertion of a long, thin and flexible probe into the mouth and down the esophagus (food tube). In the latter situation, the echocardiographic images allow the doctor to take a closer and clearer look at the valves of the heart and its chambers without interference from the chest wall.
Occasionally, a cardiologist might perform a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) to evaluate stroke or transient ischemic attack as a result of blood clots from the heart chamber. It is also useful to assess the success of previous heart procedures including valve replacements and bypass surgeries, as well as other heart conditions including congenital heart diseases.
Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) detects blood clots, tumours and abnormal masses in the heart, which may not be seen properly using standard echocardiographic images. It can also detect particular valve problems including infected heart valves.
Cardioversion, also known as electrical cardioversion, is a treatment procedure that delivers a certain level of electric current to the heart and depolarises all or most of the cardiac muscles in a momentary manner. Normal heart rhythm is then restored by the pacemaker which has the highest self-regulation (usually at the sinus node). Cardioversion is different from defibrillation. For any irregular heart rhythm which has a cardiac cycle and appears on the ECG as R wave, the delivery of the shock should correspond to the R wave on the ECG to prevent delivering during the vulnerable period of the cardiac cycle (i.e. ventricular risk zone, during that period the refractory areas of cardiac muscle are spread among non-refractory areas, which can induce ventricular fibrillation).
What is Coronary Angiogram?
Coronary angiography is an invasive test used to visualise the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. The procedure requires the injection of a special dye through a catheter (small tube) into the large artery in the wrist or occasionally in the groin. This minimally invasive procedure is performed when patient is awake under local anaesthesia. The catheter is placed at the openings of the coronary arteries before the dye is injected.
Why is Coronary Angiogram required?
Coronary angiography is an effective way to accurately detect any narrowing or blockage in the coronary arteries and other abnormalities that may be present. It allows doctor to determine the treatment that finds most appropriate to a patient. Cardiologist performs a coronary angiogram prior to angioplasty and stenting to visualise a route to guide the procedure.
What is Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)?
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a procedure used to dilate and maintain patency for any narrowing of the coronary arteries (arteries supplying blood to heart muscle). This procedure is performed with the use of X-ray and injection of a special dye through a catheter (small tube) into the large artery in the wrist or occasionally in the groin. This minimally invasive procedure is performed when patient is awake under local anaesthesia, usually after a coronary angiogram, which determines severity of the narrowing of the coronary arteries.
Why is Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) required?
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) is an effective way to relieve any narrowing or blockage in the coronary arteries that causes symptoms of angina. The procedure usually follows directly after diagnostic coronary angiogram. Coronary stents will be implanted to maintain the patency of the blocked coronary arteries.
In emergency situation caused by acute coronary syndrome (heart attack), this procedure is important and can be life saving as it can most effectively relieve the blockage in the coronary arteries caused by blood clots.
What is defibrillator?
A defibrillator is an implantable device used for treatment of abnormal heart rhythm arising from ventricle (ventricular arrhythmia). It is essentially an implantable cardiac pacemaker which consists of a battery-powered generator and leads which connect the generator to the patient’s heart. But the lead placed in the right heart has defibrillation function. As soon as a ventricular arrhythmia is detected, the ICD will automatically try to correct it by its internal algorithm or defibrillation.
Why is defibrillator required?
Heart rhythm is mainly controlled by the conduction system of the heart. Any abnormality in the conduction system may result in abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia). Life-threatening arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia (VT) and ventricular fibrillation (VF) cause not only palpitations, dizziness and syncope but also sudden death. There is evidence from various clinical trials to support the implantation of an ICD in prolonging survival among patients with a high risk of sudden cardiac death due to VT or VF. Similar to pacemaker implantation, this is a procedure performed by the cardiologist under local anaesthesia in the cardiac catheterization laboratory.
What is Permanent Cardiac Pacemaker?
A Permanent Cardiac Pacemaker is an implantable device used for long-term treatment of arrhythmias with slow heart rate. It consists of a battery-powered generator and leads which connect the generator to the patient’s heart. If the heart rate is slow, the pacemaker will stimulate the heart at a desirable rate.
Why is a Permanent Cardiac Pacemaker required?
Heart rhythm is mainly controlled by the conduction system of the heart. Any abnormality in the conduction system may result in abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia). Arrhythmias with slow heart rate cause dizziness, fainting attack (syncope), heart failure or occasionally cardiac death.
The implantation of a Permanent Cardiac Pacemaker can help to restore the heart rate back to normal so that the symptoms of dizziness or fainting attack can be relieved. This is a procedure performed by the cardiologist under local anaesthesia in the cardiac catheterization laboratory.
The size of a leadless pacemaker is the same as that of a vitamin pill. It can be directly inserted in the right ventricle of the patient, without placing any wire, through the vein in the leg. However, it is only suitable for patients who need single-chamber pacing.
What is Electrophysiological Study (EPS)?
Electrophysiological Study (EPS) is an invasive procedure that can provide specific and detailed information on the abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia), which is more superior to some other non-invasive tests. We can base on the results of EPS and offer the most appropriate treatment such as drug therapy or catheter ablation. During an attack of abnormal heart rhythm, you may have palpitation, chest discomfort, dizziness or vertigo. Occasionally, this may result in heart failure or even sudden death.
Why is Electrophysiological Study (EPS) required?
Heart rhythm is mainly controlled by the conduction system of the heart. Any abnormality in the conduction system may result in abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia). EPS is a procedure to identify the underlying cause and mechanism of abnormal heart rhythm so that further appropriate treatment including drug therapy and catheter ablation can be provided.
What is Radiofrequency Ablation / Cryoablation?
Radiofrequency Ablation / Cryoablation is a therapeutic procedure to treat abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia). It has been used for more than 20 years to treat cardiac arrhythmia. In general, there are 2 types of energy delivered during catheter ablation, namely radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation. Based on the type of abnormal heart rhythm, and the site intended to be treated, your cardiologist will choose the appropriate form of energy. This energy is released at the tip of the catheter to the abnormal heart tissue, leading to an intentional minor injury area, within which the conduction property will be lost. This aims at successful cure of the arrhythmia.
Why is Radiofrequency Ablation / Cryoablation required?
Heart rhythm is mainly controlled by the conduction system of the heart. Any abnormality in the conduction system may result in abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia). Based on the findings of EPS, which is a procedure to identify the underlying cause and mechanism of abnormal heart rhythm, catheter ablation is aimed at curing the arrhythmia that causes symptoms of palpitation, dizziness or chest discomfort, and you can avoid taking long-term anti-arrhythmic medications if a catheter ablation is successfully in treating the arrhythmia.
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a common congenital heart disease. It refers to a congenital defect at the septum which separates the left and the right atriums of the heart. As a result, there is abnormal flowing of blood from the left to the right atrium, which raises the load on the right atrium. Percutaneous Closure of ASD is performed via a percutaneous needle puncture technique through which cardiologist closes the passageway between the two atriums by inserting a closure device into the heart under the guidance of X-ray and transesophageal echocardiogram.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia or MAC. A cardiac surgeon inserts the delivery catheter into the body through a vein in the leg. Under the guidance of transseptal puncture, fluoroscopy, angiography, and transoephageal echocardiogram, cardiologist inserts the device through the delivery catheter into the left atrial appendage, where it opens up like a parachute to bond within left atrial appendage. The device acts like a natural barrier to avoid blood from staying and clotting.